(1)Morning and afternoon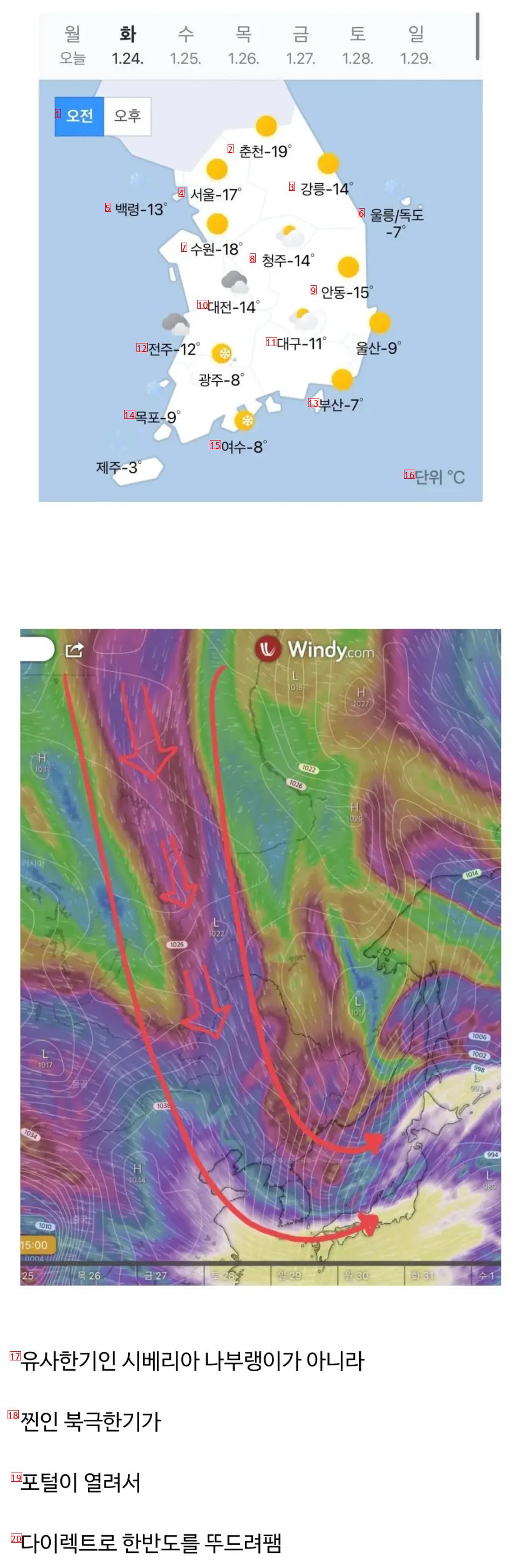
image text translation
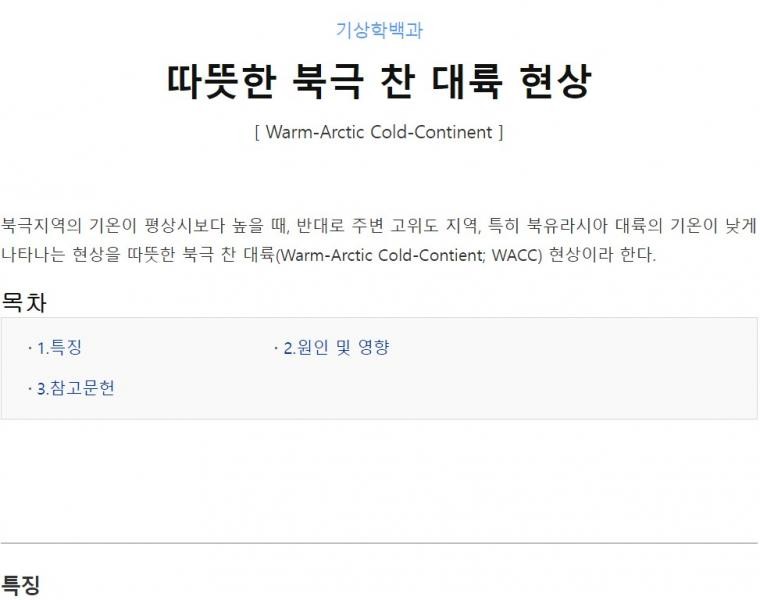
(2)Chuncheon-19°
(3)Gangneung-14°
(4)Seoul-17°
(5)White Spirit-13°
(6)Ulleung Island – 7°
(7)Water source-18°
(8)Cheongju-14°
(9)Andong-15°
(10)Daejeon-14°
(11)Daegu-11° Ulsan-9°
(12)Prelude – 12°
(13)Busan-7°
(14)Mokpo-9°
(15)Yeosu-8°
(16)Unit °C
(17)It’s not Siberian naburang, which is similar.
(18)The real Arctic cold…
(19)The portal opens.
(20)Explore the Korean Peninsula directly. Pam.
(1)Department of Meteorology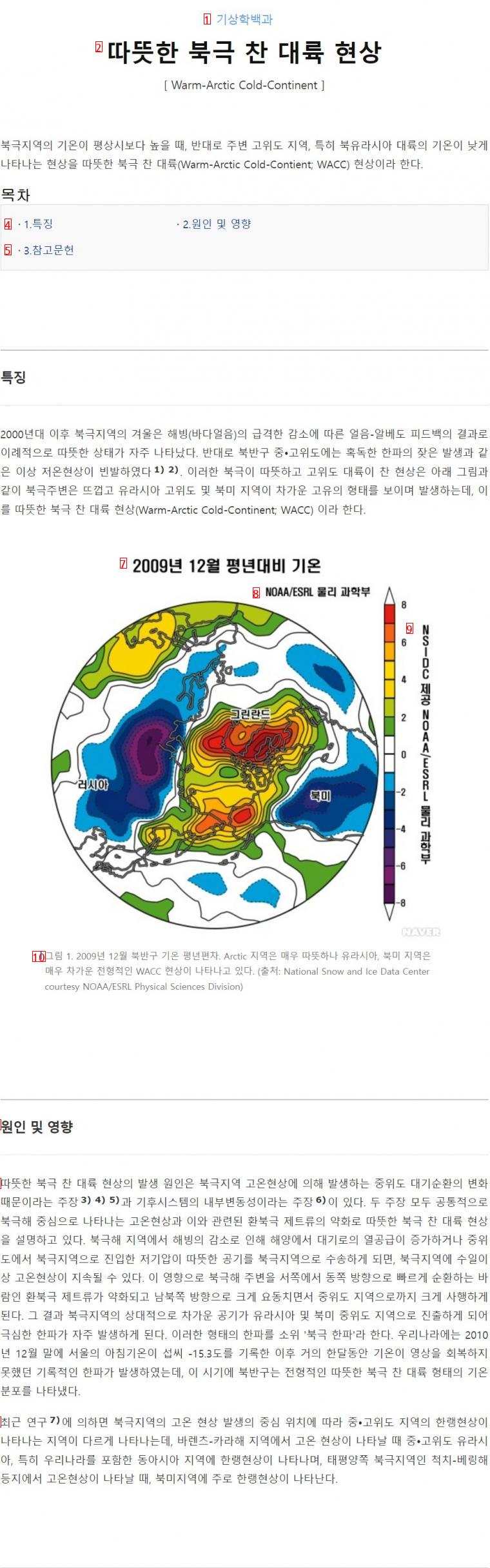
image text translation
(2)the warm Arctic cold continental phenomenon
(3)When the temperature in the Arctic is higher than usual, the temperature in the surrounding high-altitude areas, especially the North Eurasian continent, is called the warm Arctic cold-continent Warm-Arctic Cold-Content; WACC phenomenon.
(4)1 Characteristics and 2 Causes and Effects
(5)- 3 References
(6)Since the 2000s, winters in the Arctic have been unusually warm as a result of ice-albedo feedback resulting from a sharp decline in sea ice. On the contrary, abnormal cold temperatures such as frequent severe cold waves occurred frequently in the mid- and high-altitude regions of the northern hemisphere 12 This cold phenomenon occurs in a unique form around the Arctic and high Eurasia and North America as shown below, called Warm-Arctic Cold-Contin; WACC.
(7)December 2009 Temperature compared to normal
(8)NOAAESRL Department of Physical Sciences
(9)NOAA ESRL Physical Sciences Department provided by NSIDC
(10)Figure 1 The typical WACC phenomenon in December 2009 is very warm in the Arctic region, but very cold in Eurasia and North America. 출처 National Snow and Ice Data Centercourtesy NOAAESRL Physical Sciences Division
(11)Cause and effect
(12)There are arguments 345 and 6 that the cause of the warm Arctic cold continental phenomenon is due to changes in the median atmospheric circulation caused by high temperatures in the Arctic region. Both arguments commonly describe the warm Arctic cold continental phenomenon due to the high temperature phenomenon centered on the Arctic Ocean and the weakening of the related transatlantic jet stream. A decrease in liberation in the Arctic Ocean can cause more than a few days of high temperatures in the Arctic region if heat supply from the ocean to the atmosphere increases, or if a low pressure entering the Arctic from the mid-latitude carries warm air into the Arctic region. As a result, the whirling Arctic jet stream, a wind that circulates rapidly from west to east around the Arctic Ocean, weakens and fluctuates greatly in the north-south direction, leading to a large meandering to the mid-latitude area. As a result, relatively cold air from the Arctic region enters the mid-eurasian and North American regions, resulting in frequent severe cold waves. This type of cold wave is the so-called Arctic cold wave in Korea, where temperatures have not recovered for nearly a month since the morning temperature in Seoul hit -153 degrees Celsius at the end of December 2010, when the northern hemisphere showed a typical warm Arctic cold continental temperature distribution.
(13)According to a recent study 7, cold areas in the mid- to high-altitude regions differ depending on the central location of high temperatures in the Arctic. When high temperatures occur in the Barents-Carra Sea, cold in Eurasia, especially in East Asia, including Korea, and when high temperatures occur in the Pacific Arctic, Chuck-Bering Sea.
!